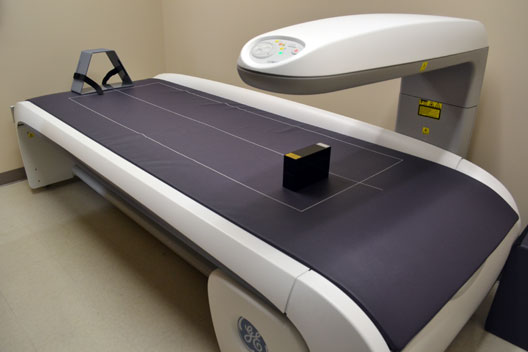
16 Feb CTSI Bionutrition and Body Composition Lab Acquires Lunar iDXA
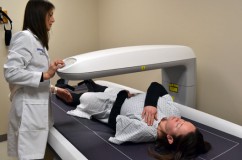
Comprehensive views and trending data of body composition are valuable in clinical research and practical applications when investigating diseases that affect bone mineral content and soft tissue. A number of conditions exist where capturing body composition and bone mineral content is significant for further understanding and finding related interventions. Some of these conditions are: nutritional disorders including malabsorption, obesity, anorexia and the athlete triad; poly cystic ovarian syndrome; glucocorticoid therapy; pulmonary disorders including COPD’s dyspnea effects on nutrition status in relation to body weight and overall health status and Cystic Fibrosis’s increased needs for energy and malabsorption effects on body composition; bone disorders; renal diseases; and hepatobiliary disorder including short and long term survival associated with malnutrition risk factors, Cirrhosis and fat distributions and loss of lean muscle. In order to further assist investigators with their research of such conditions, the CTSI Bionutrition and Body Composition Lab has acquired a GE Medical Systems Lunar iDXA.
The dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) assesses bone mineral density and has advanced abilities as a three compartment model to measure body composition. It is equipped with enCORE software that includes many features for total body bone mineral density as well as various anatomical sites. It also identifies vertebral deformation, relative fracture risk and total body composition measurements with specific features to measure and analyze android fat, gynoid fat and estimate visceral fat.
Determining body fat distribution when assessing risk factors of different diseases can provide investigators with valuable information about conditions such as obesity, anorexia nervosa, cystic fibrosis, chronic renal failure and wasting syndrome (caused by HIV/Aids). “The DXA can measure android and gynoid regions and from that estimate visceral fat, a predictor of obesity related health risks such as, hypertension, diabetes mellitus type two, coronary heart disease, dyslipidemia and premature death.” said Andrea Moosreiner, RD, CD, CTSI Bionutritionist. “DXA scans have significantly improved over the past few years and are now alternatives to CT scans, X-rays, and MRIs for accurately measuring body composition. The Lunar iDXA is equipped with SmartScan which only scans the area of interest lowering the radiation dose and shortening scan time.” For more information or to access the iDXA, complete a request for space and services on the CTSI website.